Polyethylene plastic
(1) Introduction Polyethylene is a polymer of ethylene monomer. The raw materials for production are petroleum, coke oven gas or alcohol. Industrial production of polyethylene is generally obtained by dehydration of ethanol, catalytic hydrogenation of acetylene or pyrolysis. Its trade name is abbreviated as “B-plasticâ€; the English abbreviation is PE. Due to the different density of polyethylene, it is divided into low density polyethylene. [PE (L)], medium density polyethylene [PE (M)] and high density polyethylene [PE (H)]. The molecular structure of polyethylene is: (—CH 2 —CH 2 —) n. It is a linear geometry that theoretically has no branches and is prone to crystallization. Generally, the polyethylene macromolecule is composed of a crystal region and an amorphous region in a high elastic state; the crystal region imparts higher hardness, strength, chemical stability, etc. to the polyethylene plastic; the amorphous region imparts a higher softness to the polyethylene plastic. Sex, resilience, transparency, etc. In fact, polyethylene macromolecules are not absolutely unbranched. The crystallinity is different, the density is also different, and the physical and mechanical properties are also different. (2) Polymerization method Low density polyethylene Also known as "high pressure soft plastic." It is prepared by polymerizing ethylene monomer with a trace amount of oxygen as an initiator at 1200 to 2000 at a temperature of 100 to 300 ° C using an oxygen, an organic peroxide or an azo compound as an initiator. 2. Medium density polyethylene The medium density polyethylene is synthesized by using chromium oxide or molybdenum oxide as a catalyst under the conditions of 30-70 atmospheres and a temperature of 100-250 °C. In practice, the following methods are used: 1 blending low density polyethylene and high density polyethylene in a certain ratio; 2 using a mud method or a solution method, which is obtained by copolymerizing ethylene with a second monomer such as propylene or butene; 3 is produced by high pressure method, which is prepared by copolymerization of ethylene with a second monomer such as vinyl acetate or acrylate, or by controlling ethylene conversion rate under relatively low conditions; 4 is obtained by gas phase method. 3. High density polyethylene It is polymerized by a catalyst composed mainly of aluminum alkyl and titanium tetrachloride under normal pressure of 10 atm and 60-80 °C. (three) performance Physical and mechanical properties PE is milky white waxy translucent material, lighter than water, odorless, tasteless and non-toxic; HDPE soft, LDPE hard; gas permeability decreases with increasing density, permeability to N2, O2, CO2 and other films Compared with HDPE, the permeability of water vapor is relatively small; the low temperature resistance of PE is the best in general plastics, the cracking temperature is -70 °C, but it is not resistant to high temperature; the strength and hardness of HDPE are better. Good, but impact strength, poor elasticity, low transparency; LDPE is the opposite. MDPE performance is somewhere in between 2. Chemical resistance PE can resist general acids, alkalis and salts at normal temperature, but it is not resistant to concentrated H2SO4 and HNO3. It can withstand most organic solvents below 60 °C and swell in aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons. 3. Anti-aging performance PE degrades slowly under the action of O2 in the air; the degradation is accelerated by the action of heat, ultraviolet light and high energy radiation. 4. Insulation performance The dielectric constant is small. 5. Bonding, printing, and poor colorability. (4) Combustion characteristics It is flammable, continues to burn after leaving the fire, and emits the same odor as the paraffin burns; when burning, the tip of the flame is yellow, the bottom is blue; the smoke is less; when burning, it melts, burns, and drips. (5) Use Low-density polyethylene is widely used. It can produce film and hollow containers by extrusion blow molding. Pipes can be produced by extrusion. Composite film can be produced by extrusion calendering and kraft paper. Production of various daily necessities, such as bottles, soap boxes, toys, cups, plastic flowers. Medium density polyethylene is mainly used in the production of various bottle products, hollow products, cable products and films for high speed automatic packaging. High-density polyethylene plastic has high strength and good wear resistance, so it is mainly used for making ropes, packing belts, etc., and can also make boxes, barrels, thermos bottles and the like.
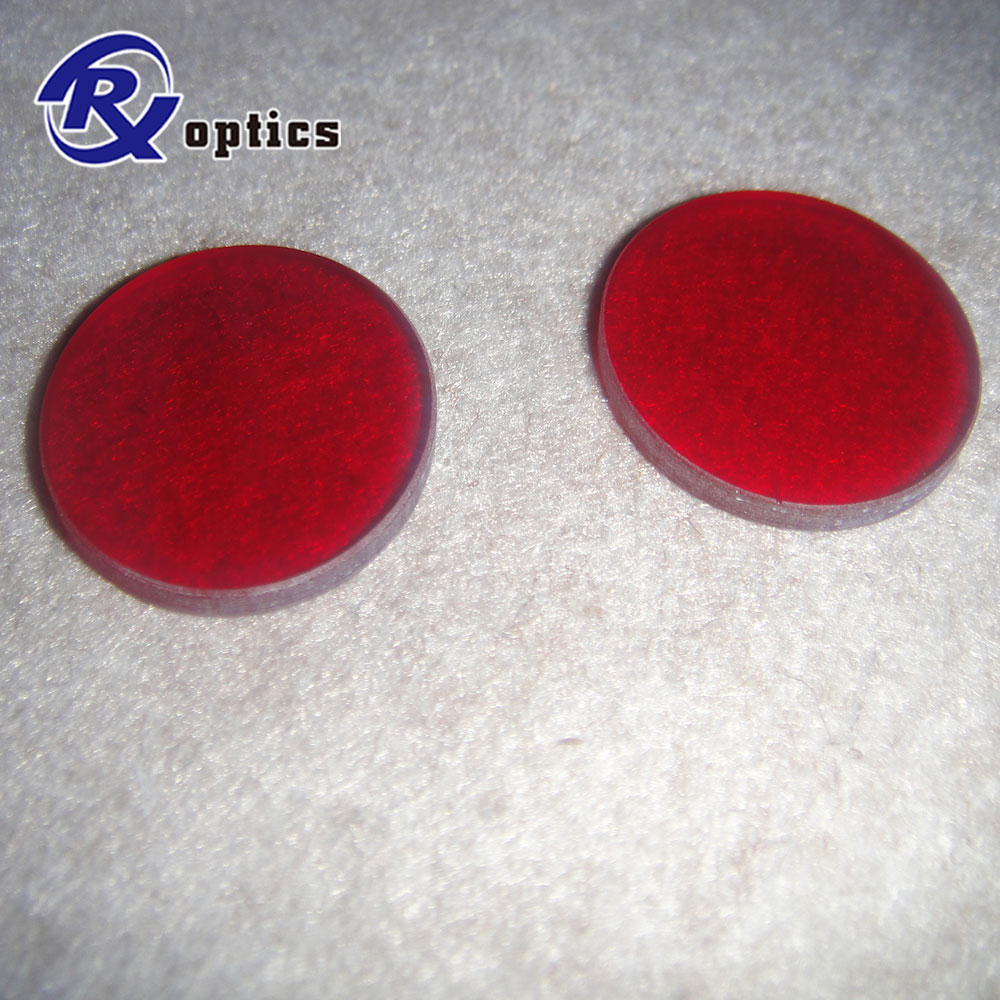
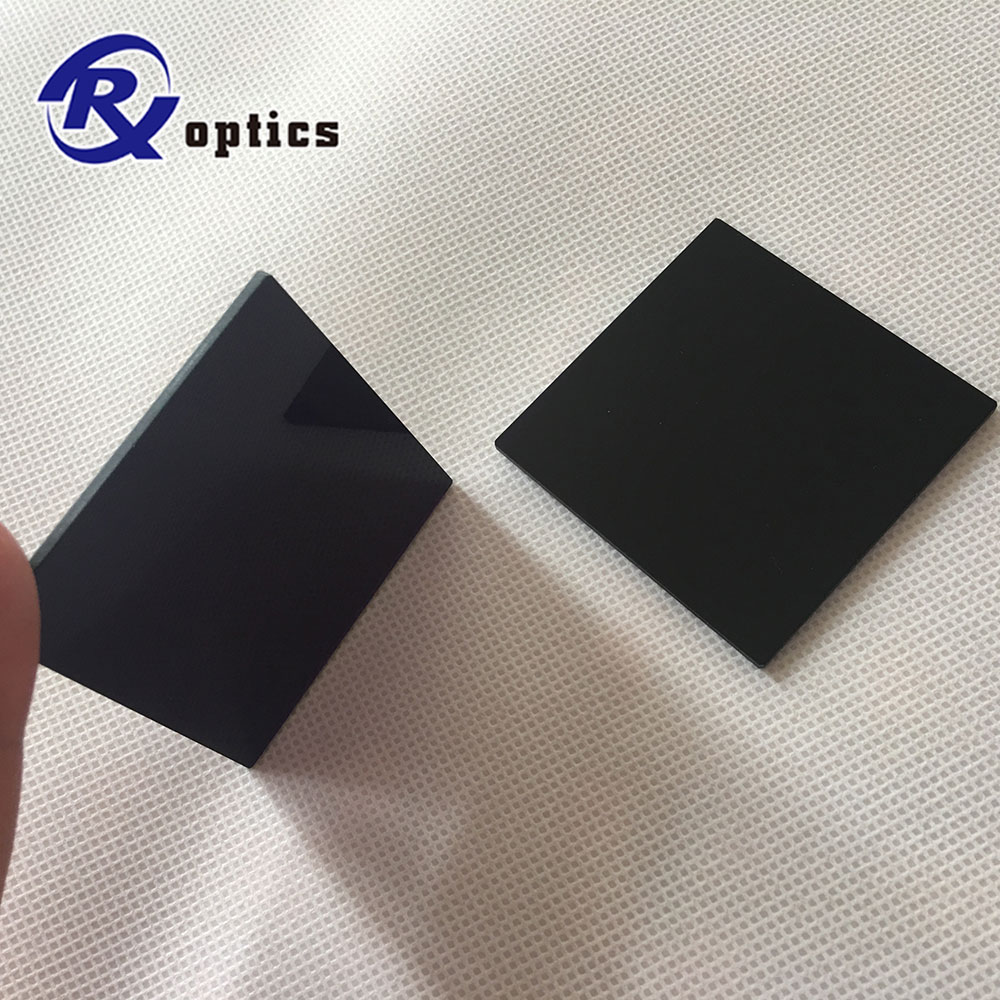
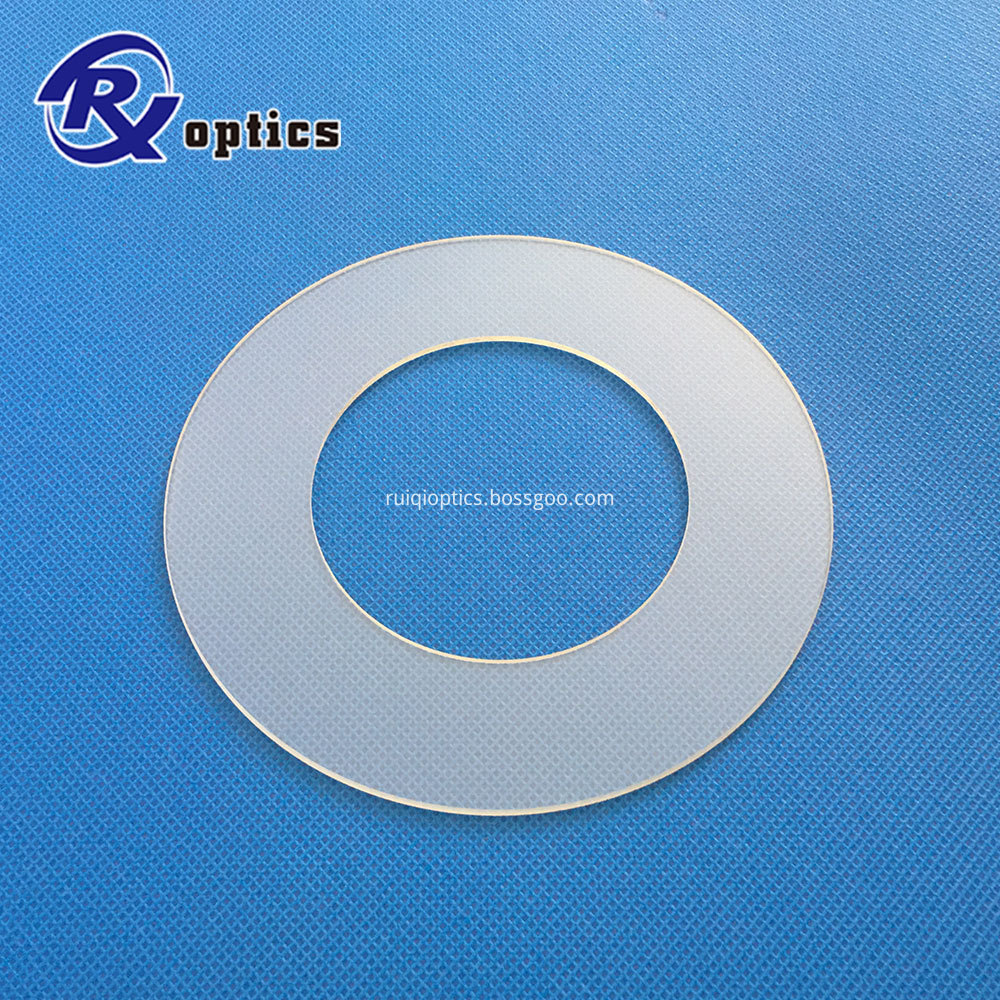
Colored Glass Filters. We provide colored glass filters for wide range of industries such as cameras, optical instruments, physics and chemistry, educational materials, industrial-use and medical-use with spectral characteristics and product size according to your requirements.
colored glass filters are manufactured from different colors of glass, such black(ZWB1, ZWB2 ZWB3), green(BG39), red(RG645, RG630,RG645), blue(QB3),yellow(JB400,JB420) etc
Optical Bandpass Filters are used to selectively transmit a portion of the spectrum while rejecting all other wavelengths. Optical
Color Glass Filter
Color Glass Filter,Black Glass Filter,Square Color Glass Filter,Optical Glass Color Filter Changchun Ruiqi Optoelectronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.ruiqi-optics.com
Bandpass Filters are ideal for a variety of applications, such as fluorescence microscopy, spectroscopy, clinical chemistry, or imaging. These filters are typically used in the life science, industrial, or R&D industries.