Correct use of diamond tools
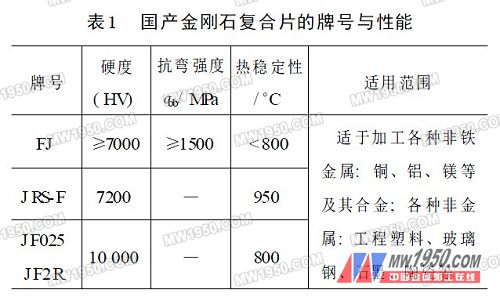
1. Type of diamond cutter There are currently four types of diamond knives commonly used in production: synthetic polycrystalline diamond (PCD) knives, synthetic polycrystalline diamond composite sheets (PCD/CC) knives, diamond coated tools, and electroplated diamond knives. Among them, the previous two types of tools are the most used. They are usually made into blades first and then fixed to the shank or body by bonding, welding or machine clamping. Diamond tools can be used to make tools such as turning tools, boring tools, milling cutters, drill bits, reamers, forming knives and cutters. (1) PCD cutter PCD is also called diamond sintered body, which is a polycrystalline material in which a plurality of synthetic diamond single crystal powders are crystallized by a metal binder such as cobalt under high temperature and high pressure. Although its hardness is slightly lower than ND, it is a polymerization of randomly oriented diamond grains, which is isotropic and can be sharply oriented when used as a cutting tool. When cutting, the cutting edge is not very sensitive to accidental damage and has a high resistance to wear. High cutting speed and large backing knife can be used in machining. The service life is generally 10 to 500 times higher than that of WC-based cemented carbide tools. The source of PCD raw materials is rich, and its price is much lower than that of ND cutters. A high performance alternative to traditional WC based carbide tools. The performance of PCD is related to the size of diamond grain synthesized by sintering polycrystal. The larger the grain size, the better the wear resistance and the higher the tool life, but the cutting edge is rough and the cutting edge quality is poor. (2) Polycrystalline diamond composite sheet (PCD/CC) cutter It is based on cemented carbide, sintered or pressed on the surface of a layer of 0.5 ~ 1mm thick PCD to form a diamond composite sheet (PCD / CC). The flexural strength of the composite sheet is basically the same as that of the cemented carbide, and the hardness of the working surface is close to the overall PCD, and the weldability is good, the regrind is easy, and the cost is low, so the application is extensive. For example, the Compax blade produced by General Electric (GE), the Syndite blade produced by DeBeers of the United Kingdom, the DA blade of Sumitomo Electric Co., Ltd., and the FJ and JRS series manufactured by China are all composite sheets of PCD and cemented carbide. Table 1 lists the grades, performance and application range of several domestic diamond composite sheets. (3) Diamond material coating tool Since diamond materials are expensive and have poor processability, it is difficult to make tools with complicated geometric shapes. In order to expand the range of applications, relatively inexpensive diamond coated tools have been developed. It is formed by depositing a film-like diamond consisting of polycrystals on a cemented carbide substrate (usually a K-type alloy) by a CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) method with a thickness of less than 50 μm (usually 10 to 30 μm). Because the base is easy to make complex shapes, it is suitable for tools with complex geometry, such as taps, drills, end mills and indexable inserts with chipbreakers. Diamond tool coating (CD) tools (such as CD1810 from Sweden's Sandvik and KCD25 from Kennametal, USA) are used in the international tool market for high-speed precision machining of non-ferrous and non-metallic materials. Layers of carbide tools are nearly ten times higher, some even dozens of times. However, CD cutters are not suitable for processing metal-based composite materials because the hard particles in the composite will wear a coating on the surface of the tool in a short time. Therefore, although the price of CD cutters is lower than that of similar PCD cutters, its wide application due to the small adhesion between the diamond film and the base material. In addition to the above-mentioned thin film coating (CD) tools, there are also CVD diamond thick film (TFD) tools. TFD is a thick film without a substrate deposited to a thickness of 1mm or more, even a few millimeters (DeBeers can be deposited up to 5mm). The thick film is cut into small pieces as needed and then brazed to the required substrate. The tool is used on the material. TFD has a good comprehensive performance. It combines the advantages of natural diamond and synthetic polycrystalline diamond. It is firmly bonded to the substrate and is easy to re-grind many times. Therefore, it has good application value and development prospects. Compared with PCD, TFD contains a metal binder such as cobalt in PCD, but cobalt will reduce the hardness of PCD and be sensitive to corrosion (especially when processing plastics). Cobalt accelerates the conversion of diamond to graphite at high temperatures, so PCD is suitable. Roughing and where the tool is required to have high fracture toughness. TFD is pure diamond material, without adding any composite material, so it has higher hardness, thermal conductivity, compactness, sharpness and wear resistance (1 to 4 times of PCD) and high temperature resistance than PCD. , chemical stability and a smaller friction factor, so the cutting speed can be higher than the PCD tool, the toughness is slightly lower than the PCD, so it is often used in high-speed finishing and semi-finishing. Foreign TFD products (such as DeBeers' DIAFILM brand). (4) Electroplated diamond cutter The electroplated diamond tool is a method of burying sand by electroplating. The metal nickel, copper and cobalt are used as a bonding agent, and a large amount of fine particles of diamond are encapsulated on the surface of the tool base of a certain size and geometry, and then subjected to appropriate grinding. to make. This method is simple in manufacturing process and requires only electroplating equipment. For example, the electroplated diamond reamer produced by Zhengzhou Abrasives Grinding Research Institute and Shandong Penglai Diamond Tool Factory belongs to this type of tool. The use shows that it is possible to successfully process holes having a dimensional accuracy and a geometric accuracy of less than 2 μm and a surface roughness value Ra of 0.4 to 0.2 μm. Moreover, the processed hole has a small dimensional dispersion, a long tool life (average 10,000 to 20,000 workpieces per tool) and high work efficiency. For example, it is widely used in various precision holes in valve bores, mechanical and precision instruments for hydraulic servo systems and fuel system precision parts. Most of the final processes in production are currently processed with such reamer. Next page Kn95 Mask,Kn95 3D Mask,Kn95 Face Mask,Kn95 Respirator Ningbo Autrends Prevention Products Co., Ltd , https://www.autrendsafety.com
A diamond tool is a tool that uses natural single crystal diamond (ND) and synthetic diamond (PCD) with similar properties to make a cutting part. It is especially effective when processing non-ferrous and non-metallic wear-resistant materials such as copper and aluminum with diamond tools. The cutting speed can be one order of magnitude higher than that of hard alloys (for example, the cutting speed of milling aluminum alloy is 3000-4000 m/min, even high 7000m/min), tool life is tens or even hundreds of times higher than cemented carbide. In the past, diamond tools have been mainly used for finishing. In the past ten years, due to the improvement of the production process of synthetic diamond, the purity and grain size of raw materials have been controlled. Composite materials and hot pressing processes have been adopted, and the application range has been expanded, in addition to being suitable for general use. In addition to finishing and semi-finishing, it can also be used for roughing. The diamond cutter has extremely high hardness, good wear resistance, sharp edge, small surface roughness value, low friction factor, good anti-adhesion and high thermal conductivity. It is not easy to stick to the knife and produce built-up edge when cutting. The surface quality is good. When processing non-ferrous metals, the surface roughness value can reach Rz=0.1~0.05μm, the processing precision can reach IT6~IT5, and it can effectively process non-ferrous metal materials and non-metal materials, such as non-ferrous metals such as copper and aluminum and their alloys. Ceramic, unsintered cemented carbide, various fiber and particle reinforced composites, plastics, rubber, graphite, glass and various wear resistant woods (especially solid wood and plywood, MDF and other composite materials). However, diamond cutters have poor toughness, low thermal stability, and chemical reaction when in contact with iron elements, and carbonization (ie, graphitization) at 700 to 800 ° C, which is generally not suitable for processing steel materials.