Main factors affecting phosphating
The phosphating mechanism of steel is complicated and susceptible to many factors, as follows: 2. Total acidity. Total acidity refers to the sum of phosphate, nitrate and acid. The total acidity should be controlled at the upper limit of the specified range, which can speed up the phosphating reaction and make the film crystal fine. However, in the phosphating process, due to consumption, the total degree is continuously decreased, the reaction is slower and slower, and the phosphating film layer becomes loose and rough. Zinc dihydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, and nitric acid can be added to the phosphating solution. Adjust the salt or phosphoric acid. The manganese phosphate treatment solution can be adjusted with ferric manganese phosphate, and 1.0 g/L of ferric manganese phosphate can be added to increase the total acidity by 1 point. If the total acidity is too high, the phosphating film layer will be thinned, and water may be added to the phosphating solution for dilution. 3. Acid ratio. 4. Temperature. The temperature of the phosphating solution has a great influence on the phosphating reaction. Therefore, the temperature specified by various phosphating formulas must be strictly observed in the phosphating treatment. Generally, the higher the temperature, the faster the phosphating reaction, the shorter the phosphating time, the thicker the phosphating film formed, the coarser the crystallization; the lower the temperature, the slower the phosphating reaction, and the longer the phosphating film is formed. The thinner the resulting film, the finer the crystal. However, the temperature should not be too high, otherwise the solution is unstable, the volatility is enhanced, and the solution evaporates quickly. 5. Accelerators and adjuvants. In general, an appropriate amount of oxidizing agent and accelerator are added to the phosphating solution. The main function of the oxidant is to accelerate the phosphating reaction speed; the promoter is mainly a metal salt with a low ionization tendency, which can accelerate the dissolution of the metal and promote the formation of the phosphating film. The oxidizing agent is generally nitrate, nitrite, halogenate, hydrogen peroxide, permanganate, sulfite, hydrazine, etc., and the oxidizing agent is different, and the performance of the phosphating film is also different. Accelerators generally use soluble copper salts or nickel salts, but currently there are fewer and fewer formulations using copper and nickel salts. In order to keep the acid ratio constant, a certain amount of alkali must be added as an adjuvant. The use of adjuvants cannot be added or supplemented at will, preferably at the beginning of the phosphating solution formulation. 6. Ion concentration. Phosphating solution 7. Steel composition. It is inevitable that there will be a certain amount of impurity metals in the steel, and the presence of these impurity metals will have different effects on the phosphate film. Usually, the carbon content in steel has a lot to do with the quality of the phosphate film. The phosphating film formed by phosphating of low carbon steel is finer and lighter in color; the phosphating of high carbon steel and low alloy steel is easier, but the crystal is easy to be thicker, the phosphating film is thicker and the color is darker. After quenching the cast steel, the phosphating film crystallizes finely; the unphosphorized cast steel, the phosphating film crystallizes coarser. Alloy steels containing metals such as chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, and silicon are more difficult to phosphatize. Therefore, the appropriate phosphating solution formulation and phosphating process should be selected according to the specific material composition of the steel. 8. Surface state. The surface state of the steel parts before phosphating greatly affects the quality of the phosphating film. For steel parts of the same material, different pretreatment methods are used, and the phosphating film obtained during phosphating has obvious differences. If the sandblasting method is used as the pretreatment and the pickling is not carried out, the phosphating film layer is fine and has high corrosion resistance; if it is pickled after blasting, the film layer obtained during phosphating is coarser and more porous, resistant to Corrosive is not strong. If the surface of the steel piece is washed with an organic solvent, the phosphating crystal is fine and compact, the phosphating speed is fast, and hydrogen evolution is small. The cold-worked steel parts should be pickled before phosphating to remove the surface oxide layer and activate the surface, otherwise the resulting phosphating film is thin and uneven. After the pickling, the steel piece is surface-adjusted for 1~2 minutes by the aqueous solution containing the titanium phosphate salt before phosphating, which can greatly improve the density of the phosphating film and enhance the corrosion resistance. For steel parts without surface adjustment, the quality of the phosphatized film is much different. Absorption Minibar,Hotel Mini Fridge,Living Room Fridge,Guest Room Mini Fridge Uni-Sec (Ningbo) Electronics Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.hospitalityunisec.com
1. Free acidity. Free acidity refers to the concentration of free phosphoric acid in the phosphating solution. If the free acidity is too high, the reaction between steel and phosphating solution is accelerated, and a large amount of hydrogen is generated in the reaction, so that the phosphate at the interface of the steel solution is not saturated, and it is difficult to form a crystallization film, the film-forming structure is loose, porous, and the corrosion resistance is lowered. The phosphating time is significantly prolonged. The free acidity is too low, the reaction between steel and phosphating solution is difficult, the phosphating film is thin, and even the phosphating film cannot be formed.
When the free acidity is too high, it should be adjusted by adding zinc carbonate, manganese carbonate or sodium hydroxide to the phosphating solution; when the free acidity is too low, it can be adjusted by adding sodium dihydrogen phosphate or ferric manganese phosphate. In general, the addition of phosphoric acid 1.0g / L or solid sodium dihydrogen phosphate 6 ~ 7g / L, the free acidity can be increased by 1 point. 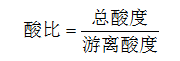
Determination of total acidity and free acidity 10.0 mL of phosphating solution can be titrated with 0.1000 mol/L sodium hydroxide standard solution. The number of milliliters consumed is expressed in points. The specific determination method is shown in the annex to this chapter.
The acid ratio of the phosphating solution is an important factor affecting phosphating. When the acid ratio is large, the phosphating reaction proceeds rapidly, and the active component of the phosphating solution is consumed quickly, and a good phosphate film is not obtained. When the acid ratio is small, the metal dissolves but does not form a phosphate film. Therefore, the acid ratio of the phosphating solution should be maintained at a suitable value. Therefore, the number of points of the acid ratio is an important factor determining the state of the phosphating treatment, and only a suitable acid ratio can obtain a uniform and smooth phosphating film layer. 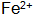 Oxidation
Oxidation 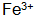 Increase the amount of sediment. Under normal circumstances, the temperature range of the impregnation method should be controlled at ±5 °C, and the injection method should be controlled at ±3 °C.
Increase the amount of sediment. Under normal circumstances, the temperature range of the impregnation method should be controlled at ±5 °C, and the injection method should be controlled at ±3 °C. 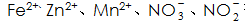 The concentration of the plasma also affects the service life of the phosphating solution and the performance of the phosphate film, and care should be taken.
The concentration of the plasma also affects the service life of the phosphating solution and the performance of the phosphate film, and care should be taken.
1) 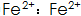 The presence of the phosphating film can increase the thickness and corrosion resistance, but is easily oxidized
The presence of the phosphating film can increase the thickness and corrosion resistance, but is easily oxidized 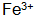 + A precipitate is formed such that a phosphate film cannot be formed. Especially in high temperature phosphating solutions or when the temperature of the phosphating solution is too high,
+ A precipitate is formed such that a phosphate film cannot be formed. Especially in high temperature phosphating solutions or when the temperature of the phosphating solution is too high, 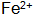 After being oxidized, the phosphating solution is turbid, which seriously affects the service life of the phosphating solution. If
After being oxidized, the phosphating solution is turbid, which seriously affects the service life of the phosphating solution. If 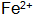 Too much, the phosphating crystal is coarse, the surface is ashed, the corrosion resistance and the heat resistance are lowered, and the phosphating solution can be removed by adding hydrogen peroxide.
Too much, the phosphating crystal is coarse, the surface is ashed, the corrosion resistance and the heat resistance are lowered, and the phosphating solution can be removed by adding hydrogen peroxide.
2) 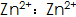 The speed of phosphating can be accelerated, the phosphating film is dense, and the gloss is good. but
The speed of phosphating can be accelerated, the phosphating film is dense, and the gloss is good. but 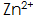 When the concentration is too high, the phosphating film will be coarse and brittle, and the surface will be gray;
When the concentration is too high, the phosphating film will be coarse and brittle, and the surface will be gray; 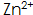 When the concentration is too low, the phosphate film layer will be loose and dull.
When the concentration is too low, the phosphate film layer will be loose and dull.
3)  The presence of the phosphating film increases the hardness, bonding strength, corrosion resistance, and deepens the color of the phosphating film. In high temperature phosphating solution
The presence of the phosphating film increases the hardness, bonding strength, corrosion resistance, and deepens the color of the phosphating film. In high temperature phosphating solution 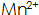 Large concentration, in medium temperature and normal temperature phosphating solution
Large concentration, in medium temperature and normal temperature phosphating solution 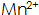 The content should not be too large, otherwise the phosphate film will not be easily formed.
The content should not be too large, otherwise the phosphate film will not be easily formed.
4) 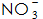 : Its role is to speed up the phosphating rate and reduce the temperature of the phosphating solution. usually,
: Its role is to speed up the phosphating rate and reduce the temperature of the phosphating solution. usually, 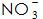 It can be reacted with Fe to form.
It can be reacted with Fe to form. 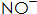 Keep phosphating solution
Keep phosphating solution 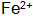 Stable.
Stable.  When the content is too high, the phosphating film is rough and thin, and yellow spots or white spots are likely to occur.
When the content is too high, the phosphating film is rough and thin, and yellow spots or white spots are likely to occur.
5) 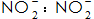 Mainly for the normal temperature phosphating solution, can accelerate the phosphating speed, promote the phosphating film crystal fine, reduce the pores, improve the corrosion resistance of the phosphating film. but
Mainly for the normal temperature phosphating solution, can accelerate the phosphating speed, promote the phosphating film crystal fine, reduce the pores, improve the corrosion resistance of the phosphating film. but 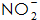 When the concentration is too large, white spots appear on the surface of the film layer.
When the concentration is too large, white spots appear on the surface of the film layer.
6)  It is an effective activator, which can accelerate the formation of phosphating crystals, form a uniform and relatively fine phosphating film, and also greatly help the corrosion resistance of the phosphating film. Especially in normal temperature phosphating solution,
It is an effective activator, which can accelerate the formation of phosphating crystals, form a uniform and relatively fine phosphating film, and also greatly help the corrosion resistance of the phosphating film. Especially in normal temperature phosphating solution, 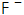 The existence is particularly important, but when the content is too high, it tends to cause white ash on the surface of the phosphating film, which also seriously affects the service life of the phosphating solution.
The existence is particularly important, but when the content is too high, it tends to cause white ash on the surface of the phosphating film, which also seriously affects the service life of the phosphating solution.
In addition, special attention needs to be paid to the phosphating solution. 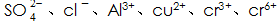 The presence of plasma will have an effect on the formation and quality of the phosphate film, and corresponding measures should be taken to reduce their content in the solution.
The presence of plasma will have an effect on the formation and quality of the phosphate film, and corresponding measures should be taken to reduce their content in the solution.
