The effect of boron on the growth of vegetables and fruits
Boron is an essential nutrient for the growth and development of vegetables. It promotes the transport and metabolism of sulfur compounds in vegetables, and promotes cell growth and cell division. Boron deficiency symptoms have been found in a variety of vegetables. Boron deficiency in vegetables leads to the wilting of stems and roots, poor flower bud differentiation, top buds and flower buds, and serious fall and fall. Symptomatic application of boron fertilizer has a significant effect on improving the yield and quality of vegetables.
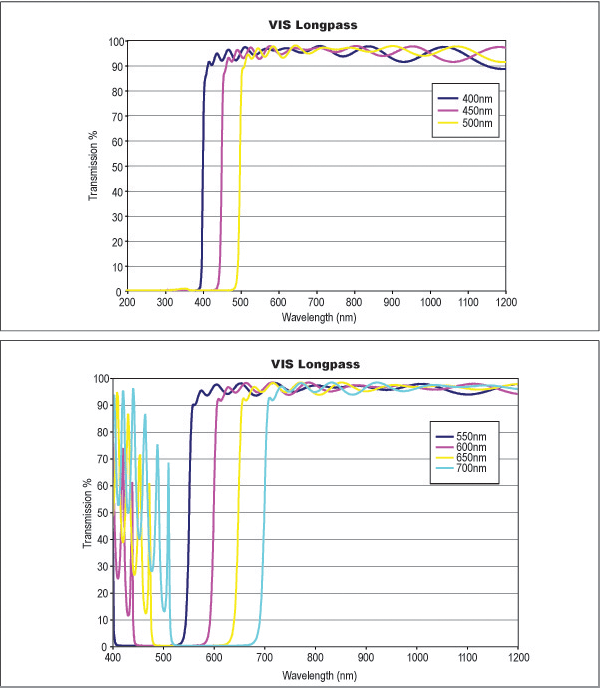
Longpass filters are designed to have a sharp transition from reflection to transmission, making them ideal for various applications. Available in a variety of cut-on wavelengths, these filters are designed for fluorescence and order sorting applications.
China star optics can supply a full range of filter. They are shortpass, longpass, bandpass, ultraviolet, infrared, heat absorbing, and color temperature conversion filters. We use material by China to Schott, Hoya, and other manufacturers to process them. Metallic films, colored glasses and thin dielectric films filter are all available per your requirements, filters are widely used in medical instrument, finance, metallurgical, photography,cameras, navigation, military, biography instrument, optical instrument andscience field etc.
Optical Longpass Filter,Optical Shortpass Filter,Colored Glass Optical Filter,Longpass Filter Kits China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.csoptlens.com
Vegetables sensitive to boron are rapeseed, broccoli, celery, radish, kale, lettuce, etc.; moderately sensitive are tomatoes, potatoes, carrots, etc.; cucumbers, onions, etc. are poorly sensitive. The typical symptoms of boron deficiency in various vegetables vary greatly. The symptoms of boron deficiency in common vegetables are as follows:
1. Cauliflower broccoli and broccoli are deficient in boron, the growth of the parietal leaves is blocked, the leaves are curled outward and deformed, and the yellow leaves begin to change from the lower leaves. The stems of the stems and flower bulbs are firstly water-soaked, and then become rust brown and wet rot, sometimes broken into hollows and cracked brown; sometimes the surface of the flower ball is also water-soaked, and then becomes rust brown.
2. Lettuce grows slowly first, the leaf edge stops growing, the top young leaves bend downward and deform, and the spots on the leaves increase to form plaques, which gradually spread to all the upper leaves, and the tip of the leaves seems to be burning. When the old leaves are deficient in boron, the symptoms are not obvious, but when the young leaves are deficient in boron, the growth point becomes curled. The center of the stem is water-soaked, and then a transverse crack occurs, and the gradient brown wet rot is ulcerated and died.
3, celery celery in the early stage of boron deficiency, brown spots along the leaves of young leaves, the tender tissue in the growth point becomes black and dead, causing heart rot. As the lesions expand, brown streaks appear on the surface of the petiole of the outer leaves, and in the case of severe, dark brown transverse cracks appear on the surface of the stem. The roots of the boron-deficient plants became brown, the lateral roots died, and the whole plant shrank in severe cases.
4, radish radish lack of boron when the growth of the upper part of the period can not see the symptoms, cross-cut after harvest can see dark brown streaks, also known as red heart disease, boiled when eaten. The heavier radish epidermis has a rough cork, and the root marrow becomes dark brown and hollow, sometimes rotted and watery.
5. The new leaves of tomato stopped growing and the plants showed atrophy. The stem is curved, the stem grows black, the new leaf grows in the lower part of the stem, and the inside of the stem is brown cork-like crack. The plants seem to be clumped, the top branches are curled and yellowed and die, the petioles become brittle, the skin appears dark spots or tissues dry, the fruit is deformed, the skin is corked, and there are brown erosion spots. The peel is cracked and the mature coloration is delayed.
6. When corn and corn are deficient in boron, the upper leaves are white with transparent stripes, the growth point is inhibited, the heading is blocked, the ear is short and curved, deformed, and the top grain is empty.
7. Fruits and vegetables are prone to male flower dysplasia, female flowers can not be produced, and the rate of falling flowers is high. There are stains on the cucumber fruit and the fruit is lignified.
Boron deficiency in fruit trees is very common. The physiological diseases caused by boron deficiency are also diverse. The following are some of the symptoms of boron deficiency in fruit trees:
1. Apple apples are deficient in boron. The top leaves of the branches are small, narrow, thick and brittle, and clustered. Some of the leaves have no serrations and shrink and wither. The veins are curved, the leaves are light green or chlorotic, showing a brown color. The petiole becomes short and brown, with early leaves. The question turns red, the side buds do not rise, or die shortly after germination. 2-5 years old big branch, there are blister-like protrusions on the sunny side, and brown spots appear in the longitudinal section of the cortex. The bark cracked and the roll fell off. Serious boron deficiency. Perennial branches, main branches and main branches have rough skin and are scab-like. The essence is black, the roots are rotten, and the whole plant is dead. Bored in boron, it is difficult to bloom normally, flower buds wither, and more flowers and fruits. Even if the fruit is fruit, some of the fruit tends to shrink, and the flesh becomes brown after the water is broken, which is sponge-like; some of the fruit shrinks.
2, the new shoots of pear pears die from the top, the amount of leaves is small, poor flowering, poor fruit. The surface of the fruit has cracking fruit, the flesh is firm and hard, the aroma is poor, the immature is yellow, the bark is festered; the pear tree is deficient in boron, and the 2-3 year old branch of the spring has a blister-like appearance, and the cortex is protruding outward. The knife can be used to remove the epidermis and the small brown spotted pear tree can be seen. When the boron deficiency is serious, the bud scale is loose, showing a semi-open state, the leaf is small, the leaf body shrinks, does not stretch, and the fruit setting rate is extremely low. The leaves on the new shoots are not normal in color and have red leaves. The main veins of the middle and lower leaves are uneven on both sides of the main vein, and the leaves are not wrinkled and the color is light. When the disease is serious, the flower buds gradually shrink and die from germination to germination. The new shoots only have a few germinations or no germination, forming bald branches and dryness; the roots are sticky, like eucalyptus bark, and many roots are rotted, leaving only the backbone roots. The fruit is short of boron in the mature stage, the fruit is small, deformed, and has a fruit-breaking phenomenon. The light-hearted vascular bundle is brown and the wood is plugged; the heavy fruit is brown, and the wood is suppository and spongy. In the fall without frost, the tips at the end of the new shoots appear red.
3. The upper part of the peach branch is dead early, the leaves become thick and brittle, and the number of side branches increases. The branches of the peach tree begin to die from the upper part and produce a large number of new branches. The new leaves become thicker and become brittle and easily broken. The branches are easy to flow; the leaves are narrow and shrinking, the petiole and veins are curved and fragile and fragile, the leaves are yellowish, the fruit is deformed, and the color is different. The lack of boron leads to weak tree, low yield and poor quality; most of the branches are dead or buds without flowers, resulting in production.
4. The young leaves of grapevine are yellow or chlorotic, the leaves and veins are chlorotic and necrotic, gradually expanding until they fall off, the flowering corolla often does not fall off, the top tendrils appear brown water stains, the growth point is necrotic, the new shoots are weak, and the knots are weak. The space is very short, the branches become brittle, and the reddish-brown corolla often does not fall off when flowering. Less fruit, a large number of non-nuclear fruit, the most obvious symptoms.
5, citrus citrus lack of boron, the leaves become smaller, there are yellow spots on the new leaves, the veins are stiff and stiff. The veins of the old leaves are cracked, and there are wood plugs. The severe veins are corked and burst, and the tops of the branches die. The leaves are not flat, and they are rolled inward and are copper yellow. The fruit has poor color, the fruit surface is not smooth, brown and black, sometimes white streaks appear, the tree is weak, and the yield is low.
6. When the peach tree is deficient in boron, the tip of the twig is dead, the leaves are deciduous, many side branches are emitted, the leaf is deformed, the leaves are small and brittle, and local concaves occur on the surface of the developing fruit, and the growth is slow.
7. The new shoots of the upper buds of the almond branches are poorly developed. Within a few months, the shoots die at the top, but the lateral branches grow drooping, and the dwarfed long branches are burned, curled, and fallen; the crown is mostly dead; the fruit is from the inside out. A brown gum appears and the fruit falls in May or June.
8, the top of the apricot shoots die, the leaves are spoon-shaped or spatula-shaped, and there is a gel. The leaf edge is curled, the tip of the leaf is necrotic, the leaf is narrowed, and it is brittle, and its veins are chlorotic. The annual branches and the two-year-old branches are severely split and fall off. In summer, many shoots die and the top leaves turn black. The epidermis of the back of the twig, petiole, main stem, and main vein also showed ulceration. The fruit setting rate is low, the fruit size, shape and color are normal, but early maturity, a few small and irregularly shaped fruit surface, there are sputum like scab, some fruits have brown lesions, and the pulp near the nucleus is especially serious.
9. When the copper is deficient in boron, the fruit will be filled with colloidal holes, and the symptoms will be different under different climatic conditions.
10, strawberry leaves shrink, cup-shaped, deformed, wrinkled, brown leaves. The vines develop very slowly and have few roots. In most cases the fruit is flattened.